Memgraph
Memgraph 是一个开源图数据库,专为动态分析环境进行了优化,并且兼容 Neo4j。要查询数据库,Memgraph 使用 Cypher——这是属性图数据库采用最广泛的、完全指定的开放查询语言。
本笔记将向您展示如何使用自然语言查询 Memgraph 以及如何从非结构化数据中构建知识图谱。
但首先,请确保您已完成所有设置。
设置
要完成本指南,您需要安装 Docker 和 Python 3.x。
首次快速运行 Memgraph Platform(Memgraph 数据库 + MAGE 库 + Memgraph Lab)时,请执行以下操作:
在 Linux/MacOS 上:
curl https://install.memgraph.com | sh
在 Windows 上:
iwr https://windows.memgraph.com | iex
这两个命令都会运行一个脚本,将 Docker Compose 文件下载到您的系统,并在两个独立的容器中构建并启动 memgraph-mage 和 memgraph-lab Docker 服务。现在,Memgraph 已经启动并运行!在 Memgraph 文档 中阅读有关安装过程的更多信息。
要使用 LangChain,请安装并导入所有必需的包。我们将使用包管理器 pip 以及 --user 标志,以确保正确的权限。如果您已安装 Python 3.4 或更高版本,则默认包含 pip。您可以使用以下命令安装所有必需的包:
pip install langchain langchain-openai langchain-memgraph --user
您既可以在此笔记本中运行提供的代码块,也可以使用单独的 Python 文件来尝试 Memgraph 和 LangChain。
自然语言查询
Memgraph 与 LangChain 的集成包含了自然语言查询功能。要使用它,请先完成所有必要的导入。我们将在代码中逐一介绍它们。
首先,实例化 MemgraphGraph。该对象管理与正在运行的 Memgraph 实例的连接。请确保正确设置所有环境变量。
import os
from langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain_memgraph.chains.graph_qa import MemgraphQAChain
from langchain_memgraph.graphs.memgraph import MemgraphLangChain
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
url = os.environ.get("MEMGRAPH_URI", "bolt://localhost:7687")
username = os.environ.get("MEMGRAPH_USERNAME", "")
password = os.environ.get("MEMGRAPH_PASSWORD", "")
graph = MemgraphLangChain(
url=url, username=username, password=password, refresh_schema=False
)
refresh_schema 的初始值被设为 False,因为数据库中尚无数据,我们希望避免不必要的数据库调用。
填充数据库
要填充数据库,首先确保它是空的。最有效的方法是切换到内存分析存储模式,删除图谱,然后返回内存事务模式。了解更多关于 Memgraph 的存储模式。
我们将添加到数据库的数据是关于不同平台上视频游戏的,这些游戏属于不同的类型,并且与发行商相关。
# Drop graph
graph.query("STORAGE MODE IN_MEMORY_ANALYTICAL")
graph.query("DROP GRAPH")
graph.query("STORAGE MODE IN_MEMORY_TRANSACTIONAL")
# Creating and executing the seeding query
query = """
MERGE (g:Game {name: "Baldur's Gate 3"})
WITH g, ["PlayStation 5", "Mac OS", "Windows", "Xbox Series X/S"] AS platforms,
["Adventure", "Role-Playing Game", "Strategy"] AS genres
FOREACH (platform IN platforms |
MERGE (p:Platform {name: platform})
MERGE (g)-[:AVAILABLE_ON]->(p)
)
FOREACH (genre IN genres |
MERGE (gn:Genre {name: genre})
MERGE (g)-[:HAS_GENRE]->(gn)
)
MERGE (p:Publisher {name: "Larian Studios"})
MERGE (g)-[:PUBLISHED_BY]->(p);
"""
graph.query(query)
[]
请注意 graph 对象是如何持有 query 方法的。该方法在 Memgraph 中执行查询,并且 MemgraphQAChain 也使用它来查询数据库。
刷新图谱模式
由于新数据是在 Memgraph 中创建的,因此有必要刷新模式。生成的模式将由 MemgraphQAChain 使用,以指导 LLM 更好地生成 Cypher 查询。
graph.refresh_schema()
为了熟悉数据并验证更新后的图表模式,您可以使用以下语句进行打印:
print(graph.get_schema)
Node labels and properties (name and type) are:
- labels: (:Platform)
properties:
- name: string
- labels: (:Genre)
properties:
- name: string
- labels: (:Game)
properties:
- name: string
- labels: (:Publisher)
properties:
- name: string
Nodes are connected with the following relationships:
(:Game)-[:HAS_GENRE]->(:Genre)
(:Game)-[:PUBLISHED_BY]->(:Publisher)
(:Game)-[:AVAILABLE_ON]->(:Platform)
查询数据库
要与 OpenAI API 交互,必须将 API 密钥配置为环境变量。这可以确保您的请求获得适当的授权。您可以在此处找到有关获取 API 密钥的更多信息。要配置 API 密钥,您可以使用 Python 的 os 包:
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "your-key-here"
如果您在 Jupyter notebook 中运行代码,请运行上面的代码片段。
接下来,创建 MemgraphQAChain,它将用于基于图数据进行问答。temperature 参数设置为零,以确保可预测和一致的答案。您可以将 verbose 参数设置为 True 以接收有关查询生成的更详细消息。
chain = MemgraphQAChain.from_llm(
ChatOpenAI(temperature=0),
graph=graph,
model_name="gpt-4-turbo",
allow_dangerous_requests=True,
)
现在您可以开始提问了!
response = chain.invoke("Which platforms is Baldur's Gate 3 available on?")
print(response["result"])
MATCH (:Game{name: "Baldur's Gate 3"})-[:AVAILABLE_ON]->(platform:Platform)
RETURN platform.name
Baldur's Gate 3 is available on PlayStation 5, Mac OS, Windows, and Xbox Series X/S.
response = chain.invoke("Is Baldur's Gate 3 available on Windows?")
print(response["result"])
MATCH (:Game{name: "Baldur's Gate 3"})-[:AVAILABLE_ON]->(:Platform{name: "Windows"})
RETURN "Yes"
Yes, Baldur's Gate 3 is available on Windows.
链修饰符
要修改链的行为并获取更多上下文或附加信息,您可以修改链的参数。
返回直接查询结果
return_direct 修饰符指定是返回执行的 Cypher 查询的直接结果,还是返回经过处理的自然语言响应。
# Return the result of querying the graph directly
chain = MemgraphQAChain.from_llm(
ChatOpenAI(temperature=0),
graph=graph,
return_direct=True,
allow_dangerous_requests=True,
model_name="gpt-4-turbo",
)
response = chain.invoke("Which studio published Baldur's Gate 3?")
print(response["result"])
MATCH (g:Game {name: "Baldur's Gate 3"})-[:PUBLISHED_BY]->(p:Publisher)
RETURN p.name
[{'p.name': 'Larian Studios'}]
返回查询中间步骤
return_intermediate_steps 链修改器通过包含查询的中间步骤以及初始查询结果来增强返回的响应。
# Return all the intermediate steps of query execution
chain = MemgraphQAChain.from_llm(
ChatOpenAI(temperature=0),
graph=graph,
allow_dangerous_requests=True,
return_intermediate_steps=True,
model_name="gpt-4-turbo",
)
response = chain.invoke("Is Baldur's Gate 3 an Adventure game?")
print(f"Intermediate steps: {response['intermediate_steps']}")
print(f"Final response: {response['result']}")
MATCH (:Game {name: "Baldur's Gate 3"})-[:HAS_GENRE]->(:Genre {name: "Adventure"})
RETURN "Yes"
Intermediate steps: [{'query': 'MATCH (:Game {name: "Baldur\'s Gate 3"})-[:HAS_GENRE]->(:Genre {name: "Adventure"})\nRETURN "Yes"'}, {'context': [{'"Yes"': 'Yes'}]}]
Final response: Yes.
限制查询结果的数量
当您想限制查询结果的最大数量时,可以使用 top_k 修改器。
# Limit the maximum number of results returned by query
chain = MemgraphQAChain.from_llm(
ChatOpenAI(temperature=0),
graph=graph,
top_k=2,
allow_dangerous_requests=True,
model_name="gpt-4-turbo",
)
response = chain.invoke("What genres are associated with Baldur's Gate 3?")
print(response["result"])
MATCH (:Game {name: "Baldur's Gate 3"})-[:HAS_GENRE]->(g:Genre)
RETURN g.name;
Adventure, Role-Playing Game
高级查询
随着解决方案复杂度的增加,您可能会遇到需要仔细处理的各种用例。确保应用程序的可扩展性对于在没有任何故障的情况下保持流畅的用户流程至关重要。
让我们再次实例化我们的链,并尝试提出一些用户可能会问的问题。
chain = MemgraphQAChain.from_llm(
ChatOpenAI(temperature=0),
graph=graph,
model_name="gpt-4-turbo",
allow_dangerous_requests=True,
)
response = chain.invoke("Is Baldur's Gate 3 available on PS5?")
print(response["result"])
MATCH (:Game{name: "Baldur's Gate 3"})-[:AVAILABLE_ON]->(:Platform{name: "PS5"})
RETURN "Yes"
I don't know the answer.
生成的 Cypher 查询看起来没问题,但我们没有收到任何响应信息。这说明了使用 LLM 时一个常见的挑战——用户提问方式与数据存储方式不匹配。在这种情况下,用户认知与实际数据存储之间的差异会导致匹配失败。提示词优化,即打磨模型的提示词以更好地理解这些差异,是一种有效的解决方法。通过提示词优化,模型在生成精确且相关的查询方面能力增强,从而成功检索到所需数据。
提示优化
为了解决这个问题,我们可以调整问答链的初始 Cypher 提示。这包括向 LLM 添加关于用户如何引用特定平台(在本例中是 PS5)的指导。我们使用 LangChain 的 PromptTemplate 来实现这一点,创建一个修改后的初始提示。然后将这个修改后的提示作为参数提供给我们的改进版 MemgraphQAChain 实例。
MEMGRAPH_GENERATION_TEMPLATE = """Your task is to directly translate natural language inquiry into precise and executable Cypher query for Memgraph database.
You will utilize a provided database schema to understand the structure, nodes and relationships within the Memgraph database.
Instructions:
- Use provided node and relationship labels and property names from the
schema which describes the database's structure. Upon receiving a user
question, synthesize the schema to craft a precise Cypher query that
directly corresponds to the user's intent.
- Generate valid executable Cypher queries on top of Memgraph database.
Any explanation, context, or additional information that is not a part
of the Cypher query syntax should be omitted entirely.
- Use Memgraph MAGE procedures instead of Neo4j APOC procedures.
- Do not include any explanations or apologies in your responses.
- Do not include any text except the generated Cypher statement.
- For queries that ask for information or functionalities outside the direct
generation of Cypher queries, use the Cypher query format to communicate
limitations or capabilities. For example: RETURN "I am designed to generate
Cypher queries based on the provided schema only."
Schema:
{schema}
With all the above information and instructions, generate Cypher query for the
user question.
If the user asks about PS5, Play Station 5 or PS 5, that is the platform called PlayStation 5.
The question is:
{question}"""
MEMGRAPH_GENERATION_PROMPT = PromptTemplate(
input_variables=["schema", "question"], template=MEMGRAPH_GENERATION_TEMPLATE
)
chain = MemgraphQAChain.from_llm(
ChatOpenAI(temperature=0),
cypher_prompt=MEMGRAPH_GENERATION_PROMPT,
graph=graph,
model_name="gpt-4-turbo",
allow_dangerous_requests=True,
)
response = chain.invoke("Is Baldur's Gate 3 available on PS5?")
print(response["result"])
MATCH (:Game{name: "Baldur's Gate 3"})-[:AVAILABLE_ON]->(:Platform{name: "PlayStation 5"})
RETURN "Yes"
Yes, Baldur's Gate 3 is available on PS5.
通过已修订的初始 Cypher prompt(其中包含平台命名指南),我们现在可以获得准确且相关的结果,更能贴合用户的查询。
这种方法可以进一步改进你的 QA 链。你可以轻松地将额外的 prompt 完善数据集成到你的链中,从而提升你的应用程序的整体用户体验。
构建知识图谱
将非结构化数据转换为结构化数据并非易事。本指南将展示如何利用 LLM 来帮助我们完成这项任务,以及如何在 Memgraph 中构建知识图谱。创建知识图谱后,您可以将其用于 GraphRAG 应用程序。
从文本构建知识图谱的步骤包括:
- 从文本中提取结�构化信息:使用 LLM 以节点和关系的形式从文本中提取结构化的图信息。
- 存储到 Memgraph:将提取的结构化图信息存储到 Memgraph 中。
从文本中提取结构化信息
除了在设置部分中的所有导入外,导入 LLMGraphTransformer 和 Document,它们将用于从文本中提取结构化信息。
from langchain_core.documents import Document
from langchain_experimental.graph_transformers import LLMGraphTransformer
下面是关于查尔斯·达尔文的示例文本(来源),将基于此构建知识图谱。
text = """
Charles Robert Darwin was an English naturalist, geologist, and biologist,
widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that
all species of life have descended from a common ancestor is now generally
accepted and considered a fundamental scientific concept. In a joint
publication with Alfred Russel Wallace, he introduced his scientific theory that
this branching pattern of evolution resulted from a process he called natural
selection, in which the struggle for existence has a similar effect to the
artificial selection involved in selective breeding. Darwin has been
described as one of the most influential figures in human history and was
honoured by burial in Westminster Abbey.
"""
下一步是使用所需的 LLM 初始化 LLMGraphTransformer 并将文档转换为图结构 LLMGraphTransformer。
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0, model_name="gpt-4-turbo")
llm_transformer = LLMGraphTransformer(llm=llm)
documents = [Document(page_content=text)]
graph_documents = llm_transformer.convert_to_graph_documents(documents)
在底层,LLM 会从文本中提取重要实体,并将它们作为节点和关系的列表返回。看起来是这样的:
print(graph_documents)
[GraphDocument(nodes=[Node(id='Charles Robert Darwin', type='Person', properties={}), Node(id='English', type='Nationality', properties={}), Node(id='Naturalist', type='Profession', properties={}), Node(id='Geologist', type='Profession', properties={}), Node(id='Biologist', type='Profession', properties={}), Node(id='Evolutionary Biology', type='Field', properties={}), Node(id='Common Ancestor', type='Concept', properties={}), Node(id='Scientific Concept', type='Concept', properties={}), Node(id='Alfred Russel Wallace', type='Person', properties={}), Node(id='Natural Selection', type='Concept', properties={}), Node(id='Selective Breeding', type='Concept', properties={}), Node(id='Westminster Abbey', type='Location', properties={})], relationships=[Relationship(source=Node(id='Charles Robert Darwin', type='Person', properties={}), target=Node(id='English', type='Nationality', properties={}), type='NATIONALITY', properties={}), Relationship(source=Node(id='Charles Robert Darwin', type='Person', properties={}), target=Node(id='Naturalist', type='Profession', properties={}), type='PROFESSION', properties={}), Relationship(source=Node(id='Charles Robert Darwin', type='Person', properties={}), target=Node(id='Geologist', type='Profession', properties={}), type='PROFESSION', properties={}), Relationship(source=Node(id='Charles Robert Darwin', type='Person', properties={}), target=Node(id='Biologist', type='Profession', properties={}), type='PROFESSION', properties={}), Relationship(source=Node(id='Charles Robert Darwin', type='Person', properties={}), target=Node(id='Evolutionary Biology', type='Field', properties={}), type='CONTRIBUTION', properties={}), Relationship(source=Node(id='Common Ancestor', type='Concept', properties={}), target=Node(id='Scientific Concept', type='Concept', properties={}), type='BASIS', properties={}), Relationship(source=Node(id='Charles Robert Darwin', type='Person', properties={}), target=Node(id='Alfred Russel Wallace', type='Person', properties={}), type='COLLABORATION', properties={}), Relationship(source=Node(id='Natural Selection', type='Concept', properties={}), target=Node(id='Selective Breeding', type='Concept', properties={}), type='COMPARISON', properties={}), Relationship(source=Node(id='Charles Robert Darwin', type='Person', properties={}), target=Node(id='Westminster Abbey', type='Location', properties={}), type='BURIAL', properties={})], source=Document(metadata={}, page_content='\n Charles Robert Darwin was an English naturalist, geologist, and biologist,\n widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that\n all species of life have descended from a common ancestor is now generally\n accepted and considered a fundamental scientific concept. In a joint\n publication with Alfred Russel Wallace, he introduced his scientific theory that\n this branching pattern of evolution resulted from a process he called natural\n selection, in which the struggle for existence has a similar effect to the\n artificial selection involved in selective breeding. Darwin has been\n described as one of the most influential figures in human history and was\n honoured by burial in Westminster Abbey.\n'))]
存储到 Memgraph
一旦您准备好 GraphDocument 格式的数据(即节点和关系),就可以使用 add_graph_documents 方法将其导入 Memgraph。该方法会将 graph_documents 列表转换为需要在 Memgraph 中执行的适当的 Cypher 查询。完成后,知识图谱就会存储在 Memgraph 中。
# Empty the database
graph.query("STORAGE MODE IN_MEMORY_ANALYTICAL")
graph.query("DROP GRAPH")
graph.query("STORAGE MODE IN_MEMORY_TRANSACTIONAL")
# Create KG
graph.add_graph_documents(graph_documents)
Memgraph Lab 中的图表显示如下(请在 localhost:3000 上查看):
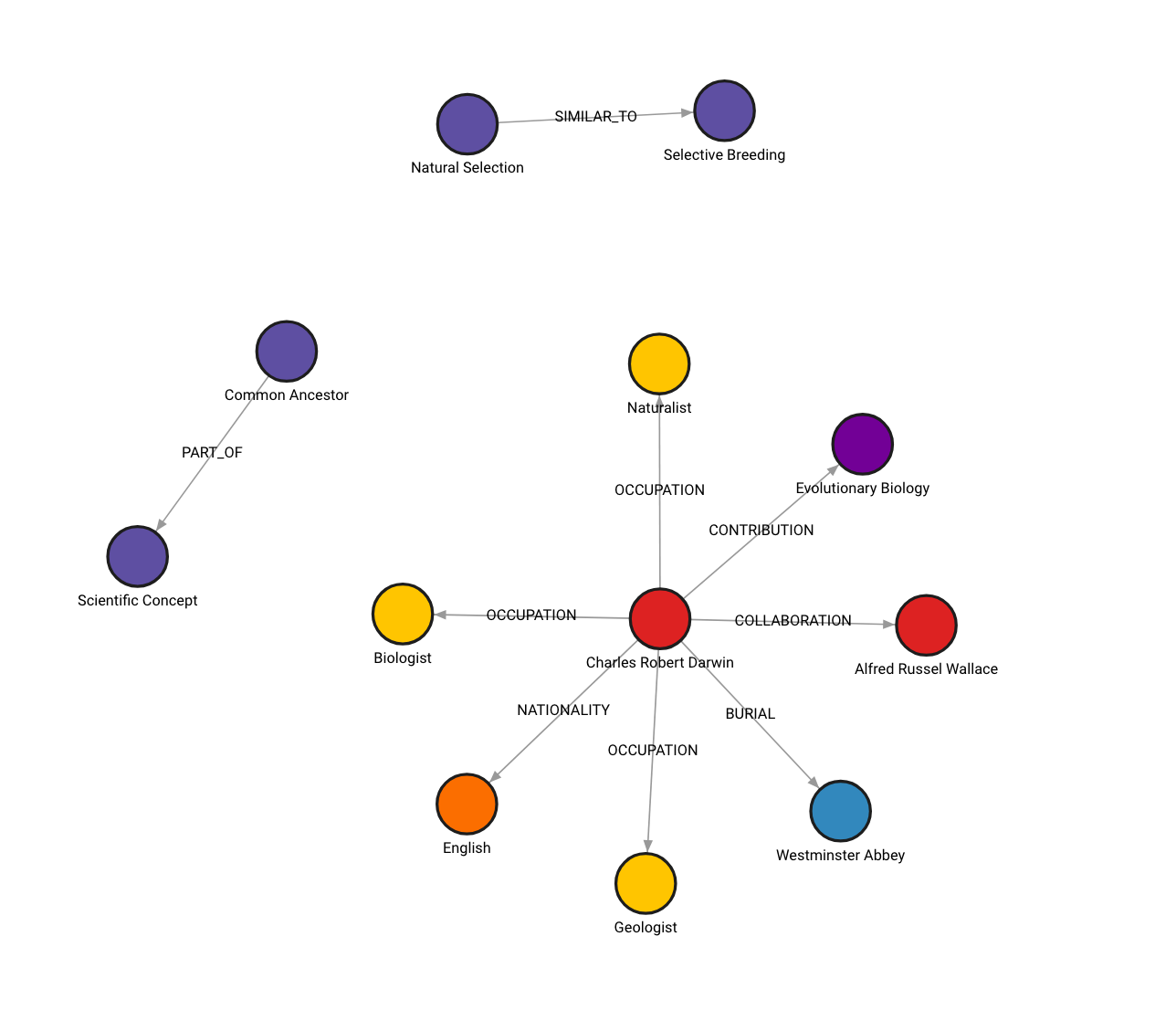
如果您尝试时得到了不同的图表,这是预期行为。图表构建过程是非确定性的,因为用于从非结构化数据生成节点和关系的 LLM 也是非确定性的。
其他选项
此外,您可以根据自己的需求灵活定义要提取的特定类型的节点和关系。
llm_transformer_filtered = LLMGraphTransformer(
llm=llm,
allowed_nodes=["Person", "Nationality", "Concept"],
allowed_relationships=["NATIONALITY", "INVOLVED_IN", "COLLABORATES_WITH"],
)
graph_documents_filtered = llm_transformer_filtered.convert_to_graph_documents(
documents
)
print(f"Nodes:{graph_documents_filtered[0].nodes}")
print(f"Relationships:{graph_documents_filtered[0].relationships}")
Nodes:[Node(id='Charles Robert Darwin', type='Person', properties={}), Node(id='English', type='Nationality', properties={}), Node(id='Evolutionary Biology', type='Concept', properties={}), Node(id='Natural Selection', type='Concept', properties={}), Node(id='Alfred Russel Wallace', type='Person', properties={})]
Relationships:[Relationship(source=Node(id='Charles Robert Darwin', type='Person', properties={}), target=Node(id='English', type='Nationality', properties={}), type='NATIONALITY', properties={}), Relationship(source=Node(id='Charles Robert Darwin', type='Person', properties={}), target=Node(id='Evolutionary Biology', type='Concept', properties={}), type='INVOLVED_IN', properties={}), Relationship(source=Node(id='Charles Robert Darwin', type='Person', properties={}), target=Node(id='Natural Selection', type='Concept', properties={}), type='INVOLVED_IN', properties={}), Relationship(source=Node(id='Charles Robert Darwin', type='Person', properties={}), target=Node(id='Alfred Russel Wallace', type='Person', properties={}), type='COLLABORATES_WITH', properties={})]
如果不这样,图形看起来会是这样:
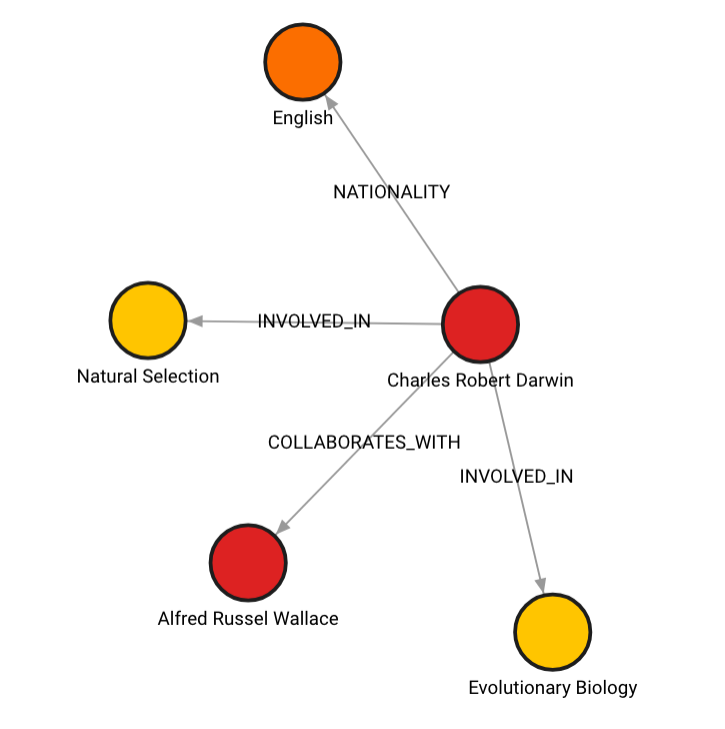
您的图形也可以在所有节点上带有 __Entity__ 标签,这些标签将被索引以加快检索速度。
# Drop graph
graph.query("STORAGE MODE IN_MEMORY_ANALYTICAL")
graph.query("DROP GRAPH")
graph.query("STORAGE MODE IN_MEMORY_TRANSACTIONAL")
# Store to Memgraph with Entity label
graph.add_graph_documents(graph_documents, baseEntityLabel=True)
图表如下所示:
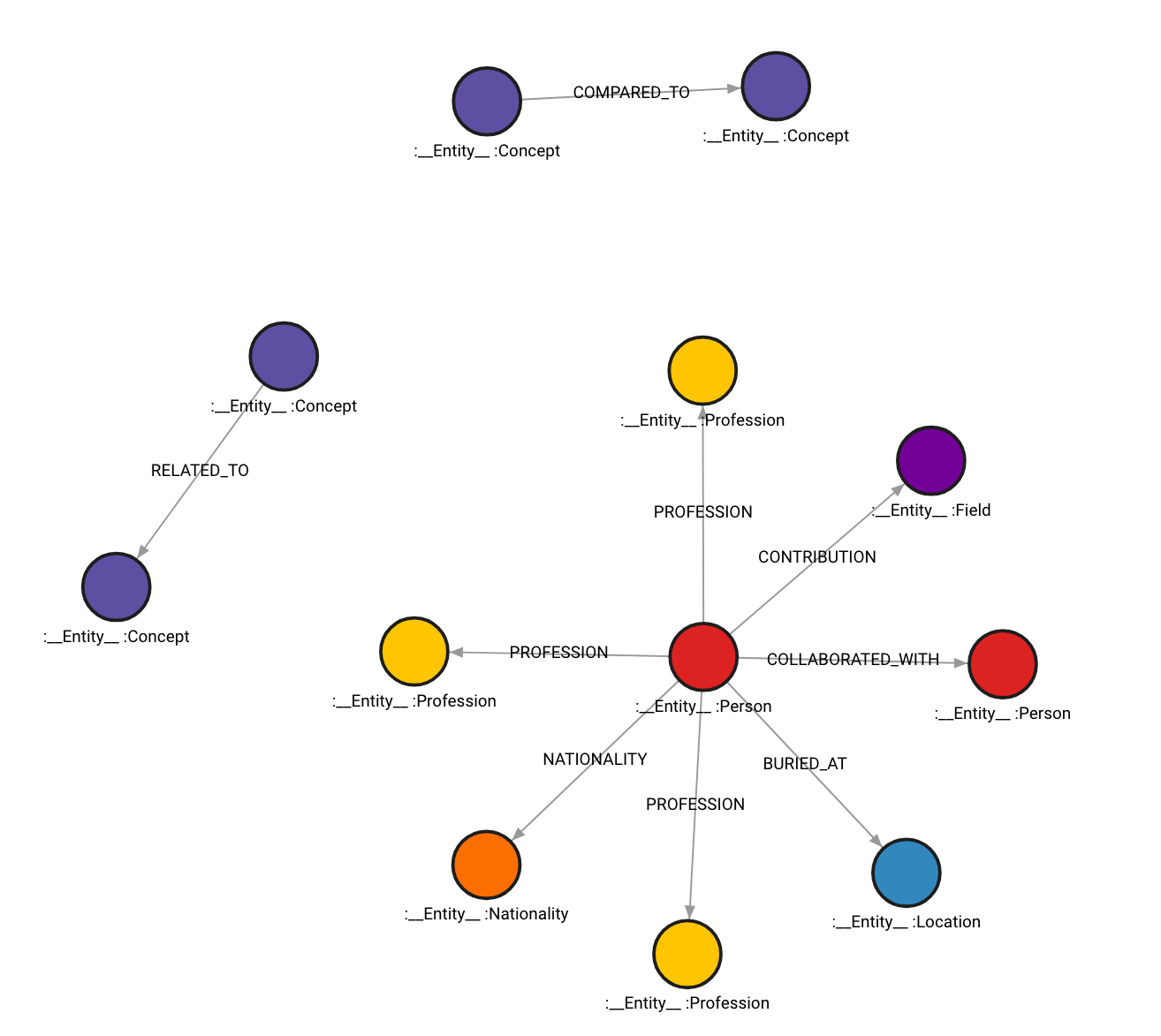
还有一个选项可以包含图形中获取的信息来源。要执行此操作,请将 include_source 设置为 True,然后将源文档存储起来,并通过 MENTIONS 关系将其链接到图中的节点。
# Drop graph
graph.query("STORAGE MODE IN_MEMORY_ANALYTICAL")
graph.query("DROP GRAPH")
graph.query("STORAGE MODE IN_MEMORY_TRANSACTIONAL")
# Store to Memgraph with source included
graph.add_graph_documents(graph_documents, include_source=True)
构建的图表如下所示:
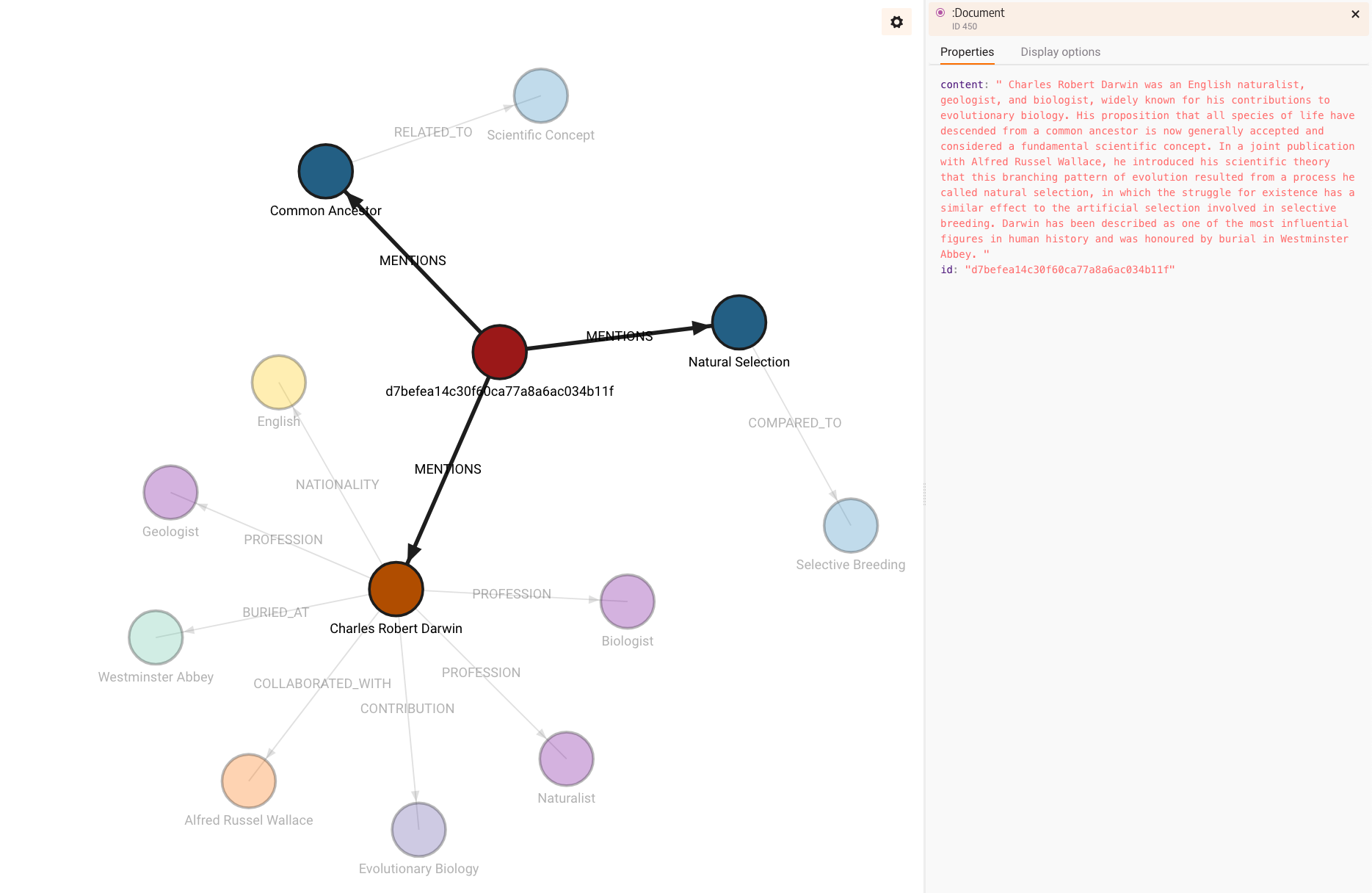
注意源内容的存储方式以及 id 属性是如何生成的,因为文档本身不包含 id。
您可以同时拥有 __Entity__ 标签和文档源。尽管如此,请注意两者都会占用内存,尤其是源内容中的长字符串。
最后,您可以像上一节所述那样查询知识图谱:
chain = MemgraphQAChain.from_llm(
ChatOpenAI(temperature=0),
graph=graph,
model_name="gpt-4-turbo",
allow_dangerous_requests=True,
)
print(chain.invoke("Who Charles Robert Darwin collaborated with?")["result"])
MATCH (:Person {id: "Charles Robert Darwin"})-[:COLLABORATION]->(collaborator)
RETURN collaborator;
Alfred Russel Wallace
