平均精确率(Mean Average Precision)¶
supervision.metrics.mean_average_precision.MeanAveragePrecision
¶
Bases: Metric
Mean Average Precision (mAP) is a metric used to evaluate object detection models. It is the average of the precision-recall curves at different IoU thresholds.
Example
import supervision as sv
from supervision.metrics import MeanAveragePrecision
predictions = sv.Detections(...)
targets = sv.Detections(...)
map_metric = MeanAveragePrecision()
map_result = map_metric.update(predictions, targets).compute()
print(map_result.map50_95)
# 0.4674
print(map_result)
# MeanAveragePrecisionResult:
# Metric target: MetricTarget.BOXES
# Class agnostic: False
# mAP @ 50:95: 0.4674
# mAP @ 50: 0.5048
# mAP @ 75: 0.4796
# mAP scores: [0.50485 0.50377 0.50377 ...]
# IoU thresh: [0.5 0.55 0.6 ...]
# AP per class:
# 0: [0.67699 0.67699 0.67699 ...]
# ...
# Small objects: ...
# Medium objects: ...
# Large objects: ...
map_result.plot()
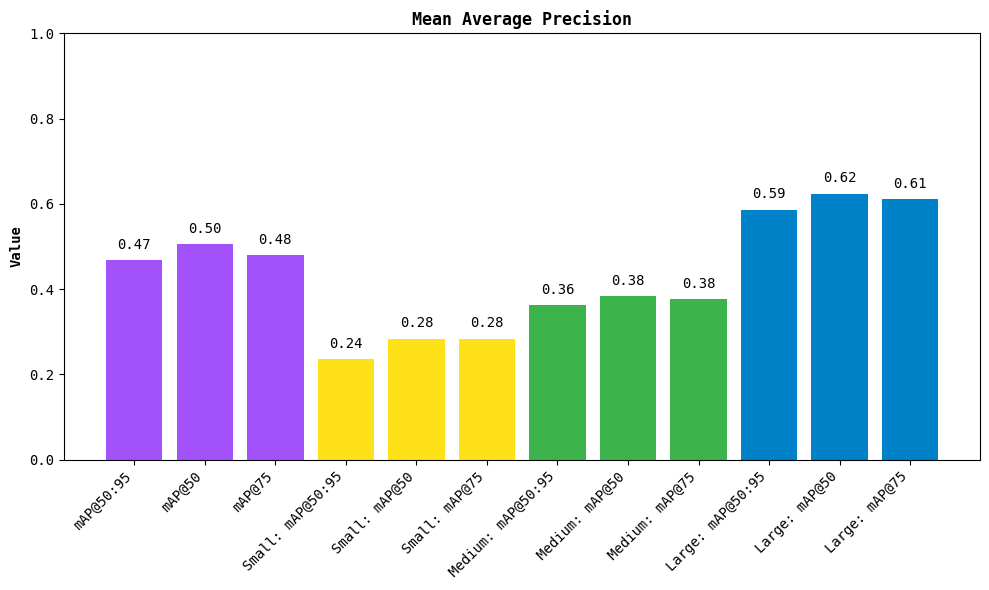
Source code in supervision/metrics/mean_average_precision.py
1097 1098 1099 1100 1101 1102 1103 1104 1105 1106 1107 1108 1109 1110 1111 1112 1113 1114 1115 1116 1117 1118 1119 1120 1121 1122 1123 1124 1125 1126 1127 1128 1129 1130 1131 1132 1133 1134 1135 1136 1137 1138 1139 1140 1141 1142 1143 1144 1145 1146 1147 1148 1149 1150 1151 1152 1153 1154 1155 1156 1157 1158 1159 1160 1161 1162 1163 1164 1165 1166 1167 1168 1169 1170 1171 1172 1173 1174 1175 1176 1177 1178 1179 1180 1181 1182 1183 1184 1185 1186 1187 1188 1189 1190 1191 1192 1193 1194 1195 1196 1197 1198 1199 1200 1201 1202 1203 1204 1205 1206 1207 1208 1209 1210 1211 1212 1213 1214 1215 1216 1217 1218 1219 1220 1221 1222 1223 1224 1225 1226 1227 1228 1229 1230 1231 1232 1233 1234 1235 1236 1237 1238 1239 1240 1241 1242 1243 1244 1245 1246 1247 1248 1249 1250 1251 1252 1253 1254 1255 1256 1257 1258 1259 1260 1261 1262 1263 1264 1265 1266 1267 1268 1269 1270 1271 1272 1273 1274 1275 1276 1277 1278 1279 1280 1281 1282 1283 1284 1285 1286 1287 1288 1289 1290 1291 1292 1293 1294 1295 1296 1297 1298 1299 1300 1301 1302 1303 1304 1305 1306 1307 1308 1309 1310 1311 1312 1313 1314 1315 1316 1317 1318 1319 1320 1321 1322 1323 1324 1325 1326 1327 1328 1329 1330 1331 1332 1333 1334 1335 1336 1337 1338 1339 1340 1341 1342 1343 1344 1345 1346 | |
Functions¶
__init__(metric_target=MetricTarget.BOXES, class_agnostic=False, class_mapping=None, image_indices=None)
¶
Initialize the Mean Average Precision metric.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
|
MetricTarget
|
The type of detection data to use. |
BOXES
|
|
bool
|
Whether to treat all data as a single class. |
False
|
|
Optional[Dict[int, int]]
|
A dictionary to map class IDs to |
None
|
|
Optional[List[int]]
|
The indices of the images to use. |
None
|
Source code in supervision/metrics/mean_average_precision.py
compute()
¶
Calculate Mean Average Precision based on predicted and ground-truth detections at different thresholds using the COCO evaluation metrics. Source: https://github.com/rafaelpadilla/review_object_detection_metrics
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
MeanAveragePrecisionResult
|
The Mean Average Precision result. |
Source code in supervision/metrics/mean_average_precision.py
1276 1277 1278 1279 1280 1281 1282 1283 1284 1285 1286 1287 1288 1289 1290 1291 1292 1293 1294 1295 1296 1297 1298 1299 1300 1301 1302 1303 1304 1305 1306 1307 1308 1309 1310 1311 1312 1313 1314 1315 1316 1317 1318 1319 1320 1321 1322 1323 1324 1325 1326 1327 1328 1329 1330 1331 1332 1333 1334 1335 1336 1337 1338 1339 1340 1341 1342 1343 1344 1345 1346 | |
reset()
¶
Reset the metric to its initial state, clearing all stored data.
update(predictions, targets)
¶
Add new predictions and targets to the metric, but do not compute the result.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Union[Detections, List[Detections]]
|
The predicted detections. |
required |
|
Union[Detections, List[Detections]]
|
The ground-truth detections. |
required |
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
MeanAveragePrecision
|
The updated metric instance. |
Source code in supervision/metrics/mean_average_precision.py
supervision.metrics.mean_average_precision.MeanAveragePrecisionResult
dataclass
¶
The result of the Mean Average Precision calculation.
Defaults to 0 when no detections or targets are present.
Attributes:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
metric_target |
MetricTarget
|
the type of data used for the metric - boxes, masks or oriented bounding boxes. |
class_agnostic |
bool
|
When computing class-agnostic results, class ID
is set to |
mAP_map50_95 |
float
|
the mAP score at IoU thresholds from |
mAP_map50 |
float
|
the mAP score at IoU threshold of |
mAP_map75 |
float
|
the mAP score at IoU threshold of |
mAP_scores |
ndarray
|
the mAP scores at each IoU threshold.
Shape: |
ap_per_class |
ndarray
|
the average precision scores per
class and IoU threshold. Shape: |
iou_thresholds |
ndarray
|
the IoU thresholds used in the calculations. |
matched_classes |
ndarray
|
the class IDs of all matched classes.
Corresponds to the rows of |
small_objects |
Optional[MeanAveragePrecisionResult]
|
the mAP results for small objects (area < 32²). |
medium_objects |
Optional[MeanAveragePrecisionResult]
|
the mAP results for medium objects (32² ≤ area < 96²). |
large_objects |
Optional[MeanAveragePrecisionResult]
|
the mAP results for large objects (area ≥ 96²). |
Source code in supervision/metrics/mean_average_precision.py
25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 | |
Functions¶
__str__()
¶
Formats the evaluation output metrics to match the structure used by pycocotools
Example
```python print(map_result)
MeanAveragePrecisionResult:¶
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.464 Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.637 Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.75 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.203 Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= small | maxDets=100 ] = 0.284 Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area=medium | maxDets=100 ] = 0.497 Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= large | maxDets=100 ] = 0.629 ```
Source code in supervision/metrics/mean_average_precision.py
plot()
¶
Plot the mAP results.

Source code in supervision/metrics/mean_average_precision.py
to_pandas()
¶
Convert the result to a pandas DataFrame.
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
DataFrame
|
The result as a DataFrame. |
Source code in supervision/metrics/mean_average_precision.py
supervision.dataset.formats.coco.get_coco_class_index_mapping(annotations_path)
¶
Generates a mapping from sequential class indices to original COCO class ids.
This function is essential when working with models that expect class ids to be zero-indexed and sequential (0 to 79), as opposed to the original COCO dataset where category ids are non-contiguous ranging from 1 to 90 but skipping some ids.
Use Cases
- Evaluating models trained with COCO-style annotations where class ids are sequential ranging from 0 to 79.
- Ensuring consistent class indexing across training, inference and evaluation, when using different tools or datasets with COCO format.
- Reproducing results from models that assume sequential class ids (0 to 79).
How it Works
- Reads the COCO annotation file in its original format (
annotations_path). - Extracts and sorts all class names by their original COCO id (1 to 90).
- Builds a mapping from COCO class ids (not sequential with skipped ids) to new class ids (sequential ranging from 0 to 79).
- Returns a dictionary mapping:
{new_class_id: original_COCO_class_id}.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
|
str
|
Path to COCO JSON annotations file |
required |
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
dict[int, int]
|
Dict[int, int]: A mapping from new class id (sequential ranging from 0 to 79) |
dict[int, int]
|
to original COCO class id (1 to 90 with skipped ids). |