基于图数据库构建问答应用
在本指南中,我们将介绍构建图数据库问答链的基本方法。这些系统允许我们针对图数据库中的数据提出问题并获得自然语言的回答。首先,我们将展示一个简单的开箱即用选项,然后使用 LangGraph 实现一个更复杂的版本。
⚠️ 安全提示 ⚠️
构建图数据库的问答系统需要执行模型生成的图查询。执行此操作存在固有风险。请确保您的数据库连接权限始终根据链/代理的需要进行尽可能严格的限制。这将减轻(但不能完全消除)构建模型驱动系统的风险。有关更通用的安全最佳实践,请参见此处。
架构
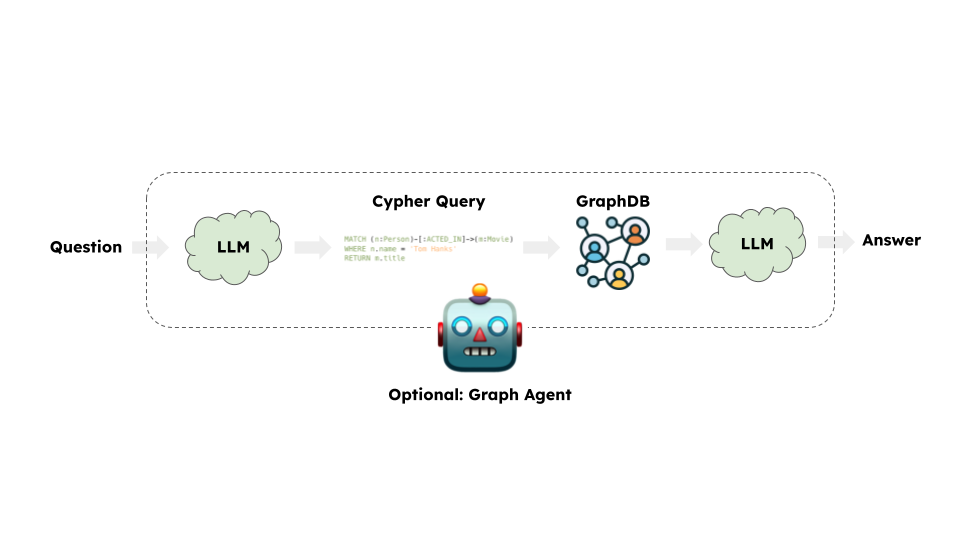
总的来说,大多数图链的步骤是:
- 将问题转换为图数据库查询: 模型将用户输入转换为图数据库查询(例如,Cypher)。
- 执行图数据库查询: 执行图数据库查询。
- 回答问题: 模型使用查询结果回应用户输入。
设置
首先,获取所需的包并设置环境变量。 在此示例中,我们将使用 Neo4j 图数据库。
%pip install --upgrade --quiet langchain langchain-neo4j langchain-openai langgraph
本指南中我们默认使用 OpenAI 模型。
import getpass
import os
if "OPENAI_API_KEY" not in os.environ:
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = getpass.getpass("Enter your OpenAI API key: ")
# Uncomment the below to use LangSmith. Not required.
# os.environ["LANGSMITH_API_KEY"] = getpass.getpass()
# os.environ["LANGSMITH_TRACING"] = "true"
Enter your OpenAI API key: ········
接下来,我们需要定义 Neo4j 凭据。 请遵循这些安装步骤来设置 Neo4j 数据库。
os.environ["NEO4J_URI"] = "bolt://localhost:7687"
os.environ["NEO4J_USERNAME"] = "neo4j"
os.environ["NEO4J_PASSWORD"] = "password"
下面的示例将创建一个与 Neo4j 数据库的连接,并用有关电影及其演员的示例文本填充它。
from langchain_neo4j import Neo4jGraph
graph = Neo4jGraph()
# Import movie information
movies_query = """
LOAD CSV WITH HEADERS FROM
'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tomasonjo/blog-datasets/main/movies/movies_small.csv'
AS row
MERGE (m:Movie {id:row.movieId})
SET m.released = date(row.released),
m.title = row.title,
m.imdbRating = toFloat(row.imdbRating)
FOREACH (director in split(row.director, '|') |
MERGE (p:Person {name:trim(director)})
MERGE (p)-[:DIRECTED]->(m))
FOREACH (actor in split(row.actors, '|') |
MERGE (p:Person {name:trim(actor)})
MERGE (p)-[:ACTED_IN]->(m))
FOREACH (genre in split(row.genres, '|') |
MERGE (g:Genre {name:trim(genre)})
MERGE (m)-[:IN_GENRE]->(g))
"""
graph.query(movies_query)
[]
图谱模式
为了让 LLM 能够生成 Cypher 语句,它需要图谱模式的信息。当你实例化一个图谱对象时,它会检索图谱模式的信息。如果你之后对图谱进行任何更改,可以运行 refresh_schema 方法来刷新模式信息。
graph.refresh_schema()
print(graph.schema)
Node properties:
Person {name: STRING}
Movie {id: STRING, released: DATE, title: STRING, imdbRating: FLOAT}
Genre {name: STRING}
Chunk {id: STRING, embedding: LIST, text: STRING, question: STRING, query: STRING}
Relationship properties:
The relationships:
(:Person)-[:DIRECTED]->(:Movie)
(:Person)-[:ACTED_IN]->(:Movie)
(:Movie)-[:IN_GENRE]->(:Genre)
如果需要更详尽的 schema 信息,可以使用 enhanced_schema 选项。
enhanced_graph = Neo4jGraph(enhanced_schema=True)
print(enhanced_graph.schema)
Received notification from DBMS server: {severity: WARNING} {code: Neo.ClientNotification.Statement.FeatureDeprecationWarning} {category: DEPRECATION} {title: This feature is deprecated and will be removed in future versions.} {description: The procedure has a deprecated field. ('config' used by 'apoc.meta.graphSample' is deprecated.)} {position: line: 1, column: 1, offset: 0} for query: "CALL apoc.meta.graphSample() YIELD nodes, relationships RETURN nodes, [rel in relationships | {name:apoc.any.property(rel, 'type'), count: apoc.any.property(rel, 'count')}] AS relationships"
``````output
Node properties:
- **Person**
- `name`: STRING Example: "John Lasseter"
- **Movie**
- `id`: STRING Example: "1"
- `released`: DATE Min: 1964-12-16, Max: 1996-09-15
- `title`: STRING Example: "Toy Story"
- `imdbRating`: FLOAT Min: 2.4, Max: 9.3
- **Genre**
- `name`: STRING Example: "Adventure"
- **Chunk**
- `id`: STRING Available options: ['d66006059fd78d63f3df90cc1059639a', '0e3dcb4502853979d12357690a95ec17', 'c438c6bcdcf8e4fab227f29f8e7ff204', '97fe701ec38057594464beaa2df0710e', 'b54f9286e684373498c4504b4edd9910', '5b50a72c3a4954b0ff7a0421be4f99b9', 'fb28d41771e717255f0d8f6c799ede32', '58e6f14dd2e6c6702cf333f2335c499c']
- `text`: STRING Available options: ['How many artists are there?', 'Which actors played in the movie Casino?', 'How many movies has Tom Hanks acted in?', "List all the genres of the movie Schindler's List", 'Which actors have worked in movies from both the c', 'Which directors have made movies with at least thr', 'Identify movies where directors also played a role', 'Find the actor with the highest number of movies i']
- `question`: STRING Available options: ['How many artists are there?', 'Which actors played in the movie Casino?', 'How many movies has Tom Hanks acted in?', "List all the genres of the movie Schindler's List", 'Which actors have worked in movies from both the c', 'Which directors have made movies with at least thr', 'Identify movies where directors also played a role', 'Find the actor with the highest number of movies i']
- `query`: STRING Available options: ['MATCH (a:Person)-[:ACTED_IN]->(:Movie) RETURN coun', "MATCH (m:Movie {title: 'Casino'})<-[:ACTED_IN]-(a)", "MATCH (a:Person {name: 'Tom Hanks'})-[:ACTED_IN]->", "MATCH (m:Movie {title: 'Schindler's List'})-[:IN_G", 'MATCH (a:Person)-[:ACTED_IN]->(:Movie)-[:IN_GENRE]', 'MATCH (d:Person)-[:DIRECTED]->(m:Movie)<-[:ACTED_I', 'MATCH (p:Person)-[:DIRECTED]->(m:Movie), (p)-[:ACT', 'MATCH (a:Actor)-[:ACTED_IN]->(m:Movie) RETURN a.na']
Relationship properties:
The relationships:
(:Person)-[:DIRECTED]->(:Movie)
(:Person)-[:ACTED_IN]->(:Movie)
(:Movie)-[:IN_GENRE]->(:Genre)
enhanced_schema 选项通过包含额外的属性信息来丰富属性信息,例如浮点数和日期的最小值和最大值,以及字符串属性的示例子。这些额外的上下文有助于引导 LLM 生成更准确、更有效的查询。
太好了!我们有了一个可以查询的图数据库。现在让我们尝试将其连接到 LLM。
GraphQACypherChain
让我们使用一个简单的开箱即用链,它接收一个问题,将其转换为 Cypher 查询,执行查询,并利用结果来回答原始问题。
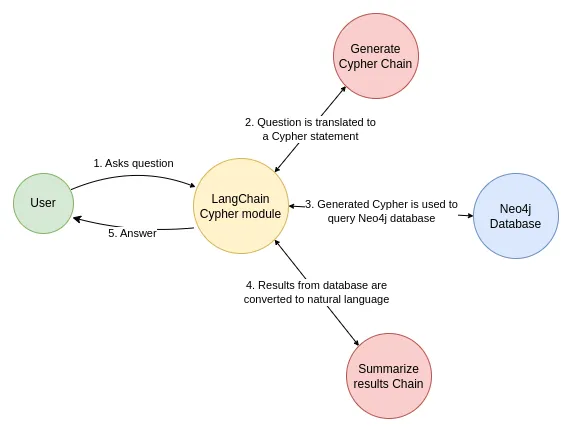
LangChain 内置了此工作流的链,专为与 Neo4j 配合使用而设计:GraphCypherQAChain
from langchain_neo4j import GraphCypherQAChain
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o", temperature=0)
chain = GraphCypherQAChain.from_llm(
graph=enhanced_graph, llm=llm, verbose=True, allow_dangerous_requests=True
)
response = chain.invoke({"query": "What was the cast of the Casino?"})
response
[1m> Entering new GraphCypherQAChain chain...[0m
Generated Cypher:
[32;1m[1;3mcypher
MATCH (p:Person)-[:ACTED_IN]->(m:Movie {title: "Casino"})
RETURN p.name
[0m
Full Context:
[32;1m[1;3m[{'p.name': 'Robert De Niro'}, {'p.name': 'Joe Pesci'}, {'p.name': 'Sharon Stone'}, {'p.name': 'James Woods'}][0m
[1m> Finished chain.[0m
{'query': 'What was the cast of the Casino?',
'result': 'Robert De Niro, Joe Pesci, Sharon Stone, and James Woods were the cast of Casino.'}
LangGraph 高级实现
GraphCypherQAChain 虽然在快速演示中很有效,但在生产环境中可能会遇到挑战。
迁移到 LangGraph 可以改进工作流程,但在生产环境中实现自然语言到查询的流程仍然是一项复杂任务。
不过,有几种策略可以显著提高准确性和可靠性,我们将在下一部分进行探讨。
以下是我们即将实现的 LangGraph 可视化流程:
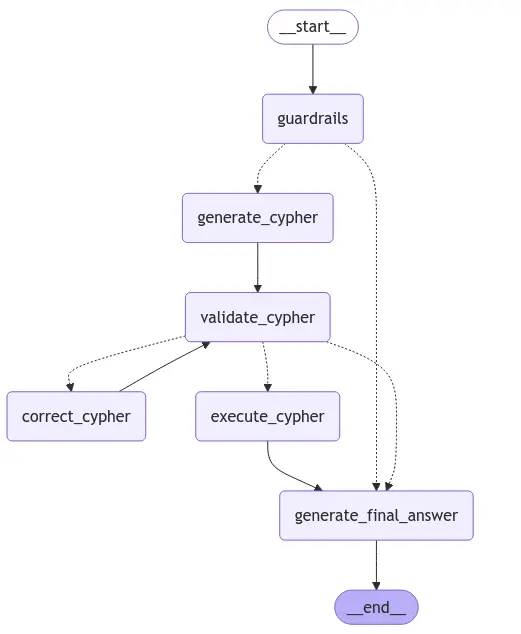
我们将从定义 LangGraph 应用程序的输入、输出和整体��状态开始。
from operator import add
from typing import Annotated, List
from typing_extensions import TypedDict
class InputState(TypedDict):
question: str
class OverallState(TypedDict):
question: str
next_action: str
cypher_statement: str
cypher_errors: List[str]
database_records: List[dict]
steps: Annotated[List[str], add]
class OutputState(TypedDict):
answer: str
steps: List[str]
cypher_statement: str
第一步是简单的 guardrails 步骤,我们在此验证问题是否与电影或其演员相关。如果不相关,我们会通知用户我们无法回答其他问题。否则,我们将进行 Cypher 生成步骤。
from typing import Literal
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
guardrails_system = """
As an intelligent assistant, your primary objective is to decide whether a given question is related to movies or not.
If the question is related to movies, output "movie". Otherwise, output "end".
To make this decision, assess the content of the question and determine if it refers to any movie, actor, director, film industry,
or related topics. Provide only the specified output: "movie" or "end".
"""
guardrails_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
(
"system",
guardrails_system,
),
(
"human",
("{question}"),
),
]
)
class GuardrailsOutput(BaseModel):
decision: Literal["movie", "end"] = Field(
description="Decision on whether the question is related to movies"
)
guardrails_chain = guardrails_prompt | llm.with_structured_output(GuardrailsOutput)
def guardrails(state: InputState) -> OverallState:
"""
Decides if the question is related to movies or not.
"""
guardrails_output = guardrails_chain.invoke({"question": state.get("question")})
database_records = None
if guardrails_output.decision == "end":
database_records = "This questions is not about movies or their cast. Therefore I cannot answer this question."
return {
"next_action": guardrails_output.decision,
"database_records": database_records,
"steps": ["guardrail"],
}
少样本提示
将自然语言转换为准确的查询具有挑战性。增强此过程的一种方法是提供相关的少样本示例来指导 LLM 进行查询生成。为了实现这一点,我们将使用 SemanticSimilarityExampleSelector 来动态选择最相关的示例。
from langchain_core.example_selectors import SemanticSimilarityExampleSelector
from langchain_neo4j import Neo4jVector
from langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
examples = [
{
"question": "How many artists are there?",
"query": "MATCH (a:Person)-[:ACTED_IN]->(:Movie) RETURN count(DISTINCT a)",
},
{
"question": "Which actors played in the movie Casino?",
"query": "MATCH (m:Movie {title: 'Casino'})<-[:ACTED_IN]-(a) RETURN a.name",
},
{
"question": "How many movies has Tom Hanks acted in?",
"query": "MATCH (a:Person {name: 'Tom Hanks'})-[:ACTED_IN]->(m:Movie) RETURN count(m)",
},
{
"question": "List all the genres of the movie Schindler's List",
"query": "MATCH (m:Movie {title: 'Schindler's List'})-[:IN_GENRE]->(g:Genre) RETURN g.name",
},
{
"question": "Which actors have worked in movies from both the comedy and action genres?",
"query": "MATCH (a:Person)-[:ACTED_IN]->(:Movie)-[:IN_GENRE]->(g1:Genre), (a)-[:ACTED_IN]->(:Movie)-[:IN_GENRE]->(g2:Genre) WHERE g1.name = 'Comedy' AND g2.name = 'Action' RETURN DISTINCT a.name",
},
{
"question": "Which directors have made movies with at least three different actors named 'John'?",
"query": "MATCH (d:Person)-[:DIRECTED]->(m:Movie)<-[:ACTED_IN]-(a:Person) WHERE a.name STARTS WITH 'John' WITH d, COUNT(DISTINCT a) AS JohnsCount WHERE JohnsCount >= 3 RETURN d.name",
},
{
"question": "Identify movies where directors also played a role in the film.",
"query": "MATCH (p:Person)-[:DIRECTED]->(m:Movie), (p)-[:ACTED_IN]->(m) RETURN m.title, p.name",
},
{
"question": "Find the actor with the highest number of movies in the database.",
"query": "MATCH (a:Actor)-[:ACTED_IN]->(m:Movie) RETURN a.name, COUNT(m) AS movieCount ORDER BY movieCount DESC LIMIT 1",
},
]
example_selector = SemanticSimilarityExampleSelector.from_examples(
examples, OpenAIEmbeddings(), Neo4jVector, k=5, input_keys=["question"]
)
接下来,我们实现 Cypher 生成链,也称为 text2cypher。提示包括增强的图谱 schema、动态选择的 few-shot 示例以及用户的提问。这种组合能够生成 Cypher 查询,以从数据库中检索相关信息。
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
text2cypher_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
(
"system",
(
"Given an input question, convert it to a Cypher query. No pre-amble."
"Do not wrap the response in any backticks or anything else. Respond with a Cypher statement only!"
),
),
(
"human",
(
"""You are a Neo4j expert. Given an input question, create a syntactically correct Cypher query to run.
Do not wrap the response in any backticks or anything else. Respond with a Cypher statement only!
Here is the schema information
{schema}
Below are a number of examples of questions and their corresponding Cypher queries.
{fewshot_examples}
User input: {question}
Cypher query:"""
),
),
]
)
text2cypher_chain = text2cypher_prompt | llm | StrOutputParser()
def generate_cypher(state: OverallState) -> OverallState:
"""
Generates a cypher statement based on the provided schema and user input
"""
NL = "\n"
fewshot_examples = (NL * 2).join(
[
f"Question: {el['question']}{NL}Cypher:{el['query']}"
for el in example_selector.select_examples(
{"question": state.get("question")}
)
]
)
generated_cypher = text2cypher_chain.invoke(
{
"question": state.get("question"),
"fewshot_examples": fewshot_examples,
"schema": enhanced_graph.schema,
}
)
return {"cypher_statement": generated_cypher, "steps": ["generate_cypher"]}
查询验证
下一步是验证生成的 Cypher 语句,确保所有属性值都准确无误。虽然数字和日期通常不需要验证,但像电影标题或人名这样的字符串则需要。在本例中,我们将使用一个基本的 CONTAINS 子句进行验证,但如果需要,也可以实现更高级的映射和验证技术。
首先,我们将创建一个链接,用于检测 Cypher 语句中的任何错误并提取它引用的属性值。
from typing import List, Optional
validate_cypher_system = """
You are a Cypher expert reviewing a statement written by a junior developer.
"""
validate_cypher_user = """You must check the following:
* Are there any syntax errors in the Cypher statement?
* Are there any missing or undefined variables in the Cypher statement?
* Are any node labels missing from the schema?
* Are any relationship types missing from the schema?
* Are any of the properties not included in the schema?
* Does the Cypher statement include enough information to answer the question?
Examples of good errors:
* Label (:Foo) does not exist, did you mean (:Bar)?
* Property bar does not exist for label Foo, did you mean baz?
* Relationship FOO does not exist, did you mean FOO_BAR?
Schema:
{schema}
The question is:
{question}
The Cypher statement is:
{cypher}
Make sure you don't make any mistakes!"""
validate_cypher_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
(
"system",
validate_cypher_system,
),
(
"human",
(validate_cypher_user),
),
]
)
class Property(BaseModel):
"""
Represents a filter condition based on a specific node property in a graph in a Cypher statement.
"""
node_label: str = Field(
description="The label of the node to which this property belongs."
)
property_key: str = Field(description="The key of the property being filtered.")
property_value: str = Field(
description="The value that the property is being matched against."
)
class ValidateCypherOutput(BaseModel):
"""
Represents the validation result of a Cypher query's output,
including any errors and applied filters.
"""
errors: Optional[List[str]] = Field(
description="A list of syntax or semantical errors in the Cypher statement. Always explain the discrepancy between schema and Cypher statement"
)
filters: Optional[List[Property]] = Field(
description="A list of property-based filters applied in the Cypher statement."
)
validate_cypher_chain = validate_cypher_prompt | llm.with_structured_output(
ValidateCypherOutput
)
大型语言模型在生成 Cypher 语句时,常常难以正确确定关系方向。由于我们能够访问模式图,我们可以使用 CypherQueryCorrector 确定性地修正这些方向。
注意:CypherQueryCorrector 是一项实验性功能,并不支持最新的所有 Cypher 语法。
from langchain_neo4j.chains.graph_qa.cypher_utils import CypherQueryCorrector, Schema
# Cypher query corrector is experimental
corrector_schema = [
Schema(el["start"], el["type"], el["end"])
for el in enhanced_graph.structured_schema.get("relationships")
]
cypher_query_corrector = CypherQueryCorrector(corrector_schema)
现在我们可以实现 Cypher 验证步骤。首先,我们使用 EXPLAIN 方法来检测任何语法错误。接下来,我们利用 LLM 来识别潜在问题并提取用于过滤的属性。对于字符串属性,我们使用简单的 CONTAINS 子句在数据库中对其进行验证。
根据验证结果,该过程可以采取以下路径:
- 如果值映射失败,我们将结束对话,并告知用户我们未能识别特定的属性值(例如,人名或电影标题)。
- 如果发现错误,我们将把查询路由进行更正。
- 如果未检测到任何问题,我们将继续进行 Cypher 执行步骤。
from neo4j.exceptions import CypherSyntaxError
def validate_cypher(state: OverallState) -> OverallState:
"""
Validates the Cypher statements and maps any property values to the database.
"""
errors = []
mapping_errors = []
# Check for syntax errors
try:
enhanced_graph.query(f"EXPLAIN {state.get('cypher_statement')}")
except CypherSyntaxError as e:
errors.append(e.message)
# Experimental feature for correcting relationship directions
corrected_cypher = cypher_query_corrector(state.get("cypher_statement"))
if not corrected_cypher:
errors.append("The generated Cypher statement doesn't fit the graph schema")
if not corrected_cypher == state.get("cypher_statement"):
print("Relationship direction was corrected")
# Use LLM to find additional potential errors and get the mapping for values
llm_output = validate_cypher_chain.invoke(
{
"question": state.get("question"),
"schema": enhanced_graph.schema,
"cypher": state.get("cypher_statement"),
}
)
if llm_output.errors:
errors.extend(llm_output.errors)
if llm_output.filters:
for filter in llm_output.filters:
# Do mapping only for string values
if (
not [
prop
for prop in enhanced_graph.structured_schema["node_props"][
filter.node_label
]
if prop["property"] == filter.property_key
][0]["type"]
== "STRING"
):
continue
mapping = enhanced_graph.query(
f"MATCH (n:{filter.node_label}) WHERE toLower(n.`{filter.property_key}`) = toLower($value) RETURN 'yes' LIMIT 1",
{"value": filter.property_value},
)
if not mapping:
print(
f"Missing value mapping for {filter.node_label} on property {filter.property_key} with value {filter.property_value}"
)
mapping_errors.append(
f"Missing value mapping for {filter.node_label} on property {filter.property_key} with value {filter.property_value}"
)
if mapping_errors:
next_action = "end"
elif errors:
next_action = "correct_cypher"
else:
next_action = "execute_cypher"
return {
"next_action": next_action,
"cypher_statement": corrected_cypher,
"cypher_errors": errors,
"steps": ["validate_cypher"],
}
Cypher 校正步骤会接收现有的 Cypher 语句、识别出的任何错误以及原始问题,从而生成查询的校正版本。
correct_cypher_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
(
"system",
(
"You are a Cypher expert reviewing a statement written by a junior developer. "
"You need to correct the Cypher statement based on the provided errors. No pre-amble."
"Do not wrap the response in any backticks or anything else. Respond with a Cypher statement only!"
),
),
(
"human",
(
"""Check for invalid syntax or semantics and return a corrected Cypher statement.
Schema:
{schema}
Note: Do not include any explanations or apologies in your responses.
Do not wrap the response in any backticks or anything else.
Respond with a Cypher statement only!
Do not respond to any questions that might ask anything else than for you to construct a Cypher statement.
The question is:
{question}
The Cypher statement is:
{cypher}
The errors are:
{errors}
Corrected Cypher statement: """
),
),
]
)
correct_cypher_chain = correct_cypher_prompt | llm | StrOutputParser()
def correct_cypher(state: OverallState) -> OverallState:
"""
Correct the Cypher statement based on the provided errors.
"""
corrected_cypher = correct_cypher_chain.invoke(
{
"question": state.get("question"),
"errors": state.get("cypher_errors"),
"cypher": state.get("cypher_statement"),
"schema": enhanced_graph.schema,
}
)
return {
"next_action": "validate_cypher",
"cypher_statement": corrected_cypher,
"steps": ["correct_cypher"],
}
我们需要添加一个执行给定 Cypher 语句的步骤。如果未返回任何结果,我们应明确处理这种情况,因为将上下文留空有时会导致 LLM 产生幻觉。
no_results = "I couldn't find any relevant information in the database"
def execute_cypher(state: OverallState) -> OverallState:
"""
Executes the given Cypher statement.
"""
records = enhanced_graph.query(state.get("cypher_statement"))
return {
"database_records": records if records else no_results,
"next_action": "end",
"steps": ["execute_cypher"],
}
最后一步是生成答案。这包括将初始问题与数据库输出相结合,以产生相关的响应。
generate_final_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
(
"system",
"You are a helpful assistant",
),
(
"human",
(
"""Use the following results retrieved from a database to provide
a succinct, definitive answer to the user's question.
Respond as if you are answering the question directly.
Results: {results}
Question: {question}"""
),
),
]
)
generate_final_chain = generate_final_prompt | llm | StrOutputParser()
def generate_final_answer(state: OverallState) -> OutputState:
"""
Decides if the question is related to movies.
"""
final_answer = generate_final_chain.invoke(
{"question": state.get("question"), "results": state.get("database_records")}
)
return {"answer": final_answer, "steps": ["generate_final_answer"]}
接下来,我们将实现 LangGraph 工作流,首先定义条件边函数。
def guardrails_condition(
state: OverallState,
) -> Literal["generate_cypher", "generate_final_answer"]:
if state.get("next_action") == "end":
return "generate_final_answer"
elif state.get("next_action") == "movie":
return "generate_cypher"
def validate_cypher_condition(
state: OverallState,
) -> Literal["generate_final_answer", "correct_cypher", "execute_cypher"]:
if state.get("next_action") == "end":
return "generate_final_answer"
elif state.get("next_action") == "correct_cypher":
return "correct_cypher"
elif state.get("next_action") == "execute_cypher":
return "execute_cypher"
现在,让我们把它们都整合起来。
from IPython.display import Image, display
from langgraph.graph import END, START, StateGraph
langgraph = StateGraph(OverallState, input=InputState, output=OutputState)
langgraph.add_node(guardrails)
langgraph.add_node(generate_cypher)
langgraph.add_node(validate_cypher)
langgraph.add_node(correct_cypher)
langgraph.add_node(execute_cypher)
langgraph.add_node(generate_final_answer)
langgraph.add_edge(START, "guardrails")
langgraph.add_conditional_edges(
"guardrails",
guardrails_condition,
)
langgraph.add_edge("generate_cypher", "validate_cypher")
langgraph.add_conditional_edges(
"validate_cypher",
validate_cypher_condition,
)
langgraph.add_edge("execute_cypher", "generate_final_answer")
langgraph.add_edge("correct_cypher", "validate_cypher")
langgraph.add_edge("generate_final_answer", END)
langgraph = langgraph.compile()
# View
display(Image(langgraph.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png()))
现在我们可以问一个不相关的问题来测试应用程序。
langgraph.invoke({"question": "What's the weather in Spain?"})
{'answer': "I'm sorry, but I cannot provide current weather information. Please check a reliable weather website or app for the latest updates on the weather in Spain.",
'steps': ['guardrail', 'generate_final_answer']}
现在让我们来问一些关于电影的相关问题。
langgraph.invoke({"question": "What was the cast of the Casino?"})
{'answer': 'The cast of "Casino" includes Robert De Niro, Joe Pesci, Sharon Stone, and James Woods.',
'steps': ['guardrail',
'generate_cypher',
'validate_cypher',
'execute_cypher',
'generate_final_answer'],
'cypher_statement': "MATCH (m:Movie {title: 'Casino'})<-[:ACTED_IN]-(a:Person) RETURN a.name"}
后续步骤
有关此类和其他图表技术,请参阅:
